

Next: Technicalities
Up: Justification of VERITAS Design
Previous: Justification of VERITAS Design
The performance characteristics required of the VERITAS array of
imaging Cherenkov telescopes are derived from its scientific goals.
VERITAS was designed to optimize sensitivity and flexibility for
observing a variety of sources, each of which may require a different
subset of capabilities (e.g., continuous monitoring, large field of
view, good flux sensitivity, large collection area, accurate angular
resolution, low energy threshold, accurate energy resolution, prompt
response, or broad energy coverage). With these features, VERITAS can
observe known and anticipated sources in several observing modes. In
addition, the array permits flexible reconfiguration to pursue
unanticipated discoveries. Briefly summarized, the VERITAS scientific
objectives are:
- AGN studies:
- The highly variable flaring activity observed in
known TeV sources suggests that continuous monitoring of many AGN,
even using instruments with somewhat reduced capabilities, may be an
efficient means of detecting these objects. The determination of
energy spectra and study of short time-scale variability require the
best energy resolution and the largest collection area achievable.
Extending the energy range to below 100GeV is crucial for detecting
high redshift objects and additional classes of AGN with cutoffs below
a few hundred GeV.
- Galactic plane survey:
- A large field of view, good flux sensitivity,
large collection area are required to discover stable and variable
sources through a large area survey. Also, broad energy coverage will
increase sensitivity to objects with a variety of emission spectra.
Because this requires substantial observing time, this survey can be
accomplished most efficiently if the array can be split into
sub-arrays.
- Unidentified EGRET sources:
- Accurate angular resolution (for
source position reconstruction), wide field of view (for poorly
constrained source positions), and low energy threshold (to detect
previously unknown pulsars) are essential to understanding the nature
of the unidentified EGRET sources.
- Supernova remnants:
- Excellent sensitivity in the 200GeV - 2TeV
energy range is needed for this task. Also required is excellent
angular resolution to study these extended sources and accurate
spectra over a broad energy range to resolve contributions to the
emission.
- EBL studies:
- Accurate energy spectra from sources at a range of
redshifts are needed to resolve the effects of attenuation of
gamma-rays by pair-production with extragalactic background light
(EBL). Large photon statistics (i.e., large effective area) and good
energy resolution are needed for accurate spectral measurements.
Also, spectroscopy in the region around 100GeV is of particular
importance for estimating the EBL spectral density in the whole
wavelength range from 0.1-100
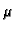 m because the amount of absorption
from the EBL is expected to rapidly decrease there.
m because the amount of absorption
from the EBL is expected to rapidly decrease there.
- GRBs:
- Prompt response to detect a rapidly decreasing flux, a
large field of view for poorly located sources, and the ability to
operate below 100GeV to extend the visibility range to high
redshifts are desired.
- Dark matter candidates:
- Broad energy coverage, good energy resolution
and good flux sensitivity are the most important requirements for
detecting a neutralino annihilation line whose specific energy and
flux is not well-constrained.
- Pulsars:
- Operation below 100GeV is required due to the expected
spectral cutoffs in these objects.
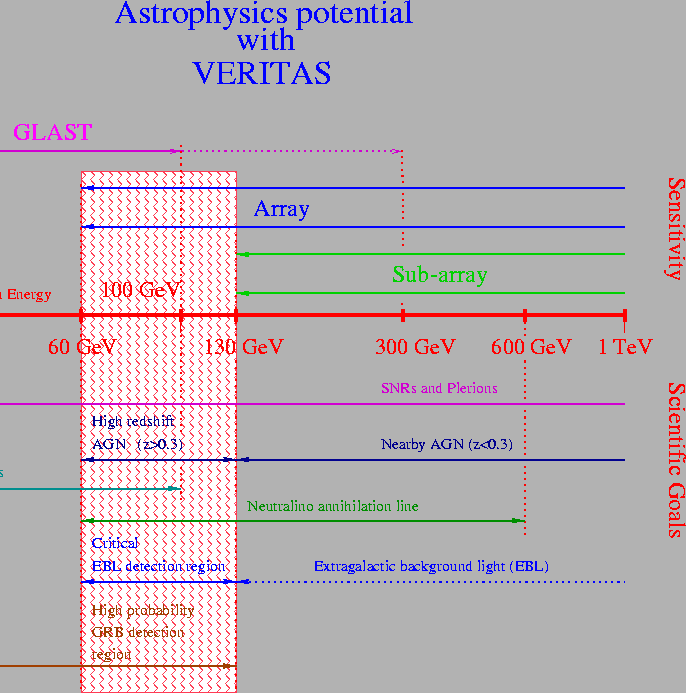
The energy ranges of these areas of interest as well as the range of
sensitivity of gamma-ray telescopes is shown in
Figure 1.
Figure 1:
Energy ranges covered with good sensitivity by the seven-telescope
VERITAS (Array), a three-telescope array (Sub-array), and GLAST
compared to the relevant energy ranges for studying some scientific
topics of interest to VERITAS. The hashed area emphasizes the region
not covered by the three-telescope sub-array.
 |


Next: Technicalities
Up: Justification of VERITAS Design
Previous: Justification of VERITAS Design
VERITAS Collaboration
